When you first read the title “How to Eat Bananas,” you might wonder why such a simple topic needs explanation. But in today’s era of modern, chemical-intensive agriculture, even a basic habit like eating a banana must be revisited from a health and safety perspective.
Bananas are a staple fruit in many households—nutritious, convenient, and widely loved. However, the growing concern around chemical residues on fruits makes it essential to understand how to consume bananas safely.

What Are Fungicides?
Fungicides are chemicals used to kill fungi. In banana cultivation, fungicides play a key role in:
- Protecting the crop from fungal diseases like Black Sigatoka and Yellow Sigatoka
- Preserving the bananas during storage and transport
- Maintaining quality and shelf life
Common fungicides used in banana farming:
- Mancozeb
- Carbendazim
- Azoxystrobin
- Propiconazole
Where and When Are Fungicides Applied?
Application areas:
- Leaves – for leaf spot diseases
- Bark – during transport and storage
- Stem – to prevent stem rot
Timing of application:
- During the growth stage
- 7–15 days before harvest
- Immediately after harvest
- Before packaging
Health Effects of Fungicide Exposure
Immediate Effects:
- Skin irritation
- Eye irritation
- Breathing difficulties
- Digestive issues
Long-Term Effects:
- Hormonal imbalances
- Nervous system disorders
- Circulatory system disturbances
- Potential cancer risk with prolonged exposure
How to Eat Bananas Safely
1. Choosing the Right Banana
Look for:
- Uniform yellow color
- Blemish-free skin
- Firm, but not overly soft texture
- Natural sweet smell
Avoid bananas with:
- Unusual color patches
- White powdery surface (possible chemical residue)
- Excessive artificial shine
- Chemical or pungent odor
- Blue or black unnatural spots
2. Safe Preparation at Home
Washing Method:
- Rinse bananas gently in clean water
- Do not use soap – chemicals may seep through the skin
- Wipe with a clean, dry cloth
Storage Tips:
- Store in a well-ventilated place
- Keep away from other fruits (to avoid ripening gases like ethylene)
- Avoid plastic bags for storage – they trap moisture and accelerate spoilage
3. Eating with Precautions
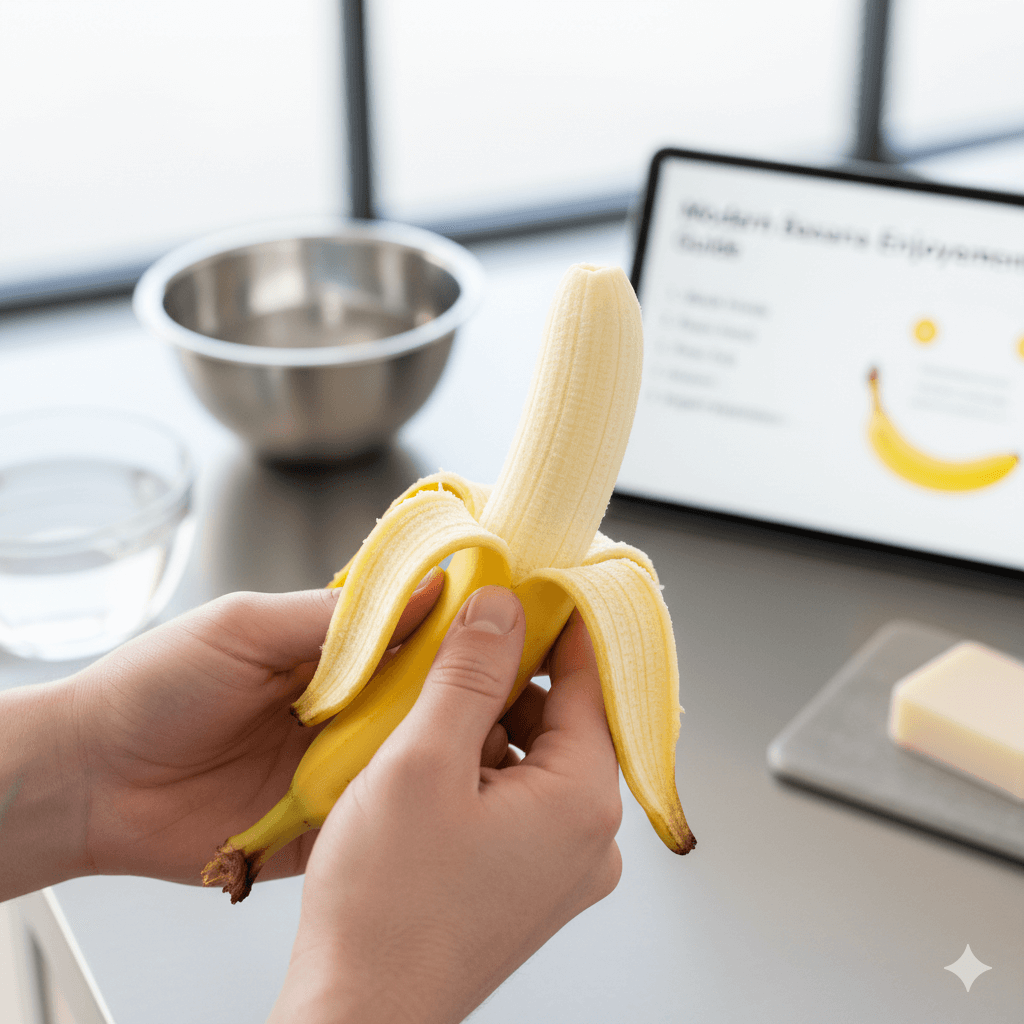
Peeling Technique:
- Start peeling from the stem end (top)
- Ensure the entire peel is removed cleanly
- Wash your hands after peeling
Avoid:
- Peeling the banana and cutting it into pieces for long storage – may expose fruit to contaminants
- Touching the banana flesh with hands that handled the peel
- Letting banana peel get under your fingernails
Tip for Children:
Adults should always peel bananas for children to ensure cleanliness and safety.
n ancient times, food was naturally safe. But with the rise of chemical farming, being aware and cautious has become essential—even with a simple fruit like the banana.
By choosing wisely, washing correctly, and handling hygienically, you can enjoy the full nutritional benefits of bananas while minimizing any health risks associated with chemical exposure.
By Dr. Ravikiran Patwardhan
Ayurvedic Doctor,
Email: patdrravi5 [email protected]